- Home
- /
- Services
- /
- Laboratories
- /
- Chemistry Lab
Chemistry Lab
Chemical Testing Laboratory Services

The AET Chemistry Laboratory provides a full suite of analytical, forensic, and standardized testing services in support of the construction industry.
Our state-of-the-art chemical testing laboratory in Saint Paul, Minnesota is equipped for traditional (“wet”) and instrumental analyses. We provide a full suite of organic and inorganic analyses of portland cement and cementitious products including concrete and mortar, for engineers, architects, building owners, manufacturers, government agencies, product developers and state departments of transportation as well as other chemists and petrographers.
We are really two types of labs — both a routine standardized testing lab as well as a one-stop-shop for non-standardized testing used in failure analysis and product testing. We support clients across the U.S. and internationally.
Often working in collaboration with our Petrography Group, Asphalt Lab and Cement/Concrete Lab, we provide routine standardized tests for acceptance, conformance, optimization, as well as product support testing, failure analyses, and forensic investigations.
AET performs analytical services and testing following ASTM, FHWA, EPA, APHA, AASHTO and other standard American and international published methods.
We provide chemical analysis of portland cement for cement manufactures using X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) equipment, which has been qualified with NIST standards to exceed ASTM C150 protocols for Portland cement.
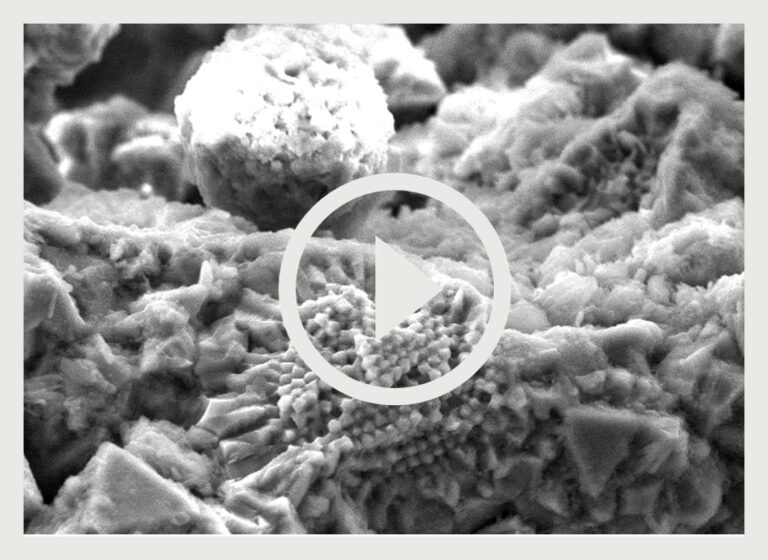
We are equipped with Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry (FTIR), X-ray Diffraction (XRD), X-ray Fluorescence (XRF), TGA Thermogravimetric Analysis, XRD X-Ray Diffraction , and SEM Scanning Electron Microscopy, LIBS Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy which, along with wet chemistry, expand our testing and analyses capabilities to include paints, flooring, adhesives and other materials related to concrete — including the identification of unknown materials.
We focus our combined 80 years of experience in independent testing, formulation, manufacturing and production to offer a one- stop solution that serves the needs of contractors, engineers, lawyers, manufacturers and other laboratories.
AET’s Chemistry services add value to client projects by not only providing routine chemical testing and analysis, but also by helping clients determine how testing can be designed and utilized to best serve their particular needs.
When needed, such as in forensic investigations, we collaborate with our Petrography Group, Asphalt Lab and Cement/Concrete Lab to help identify the source of a problem, what happened, and how to reduce re-occurrences. Our results also help clients improve their products or uses of their materials.
Construction and Building Materials Analyzed
- Adhesives
- Caulks and Sealants
- Chemical admixture and additives
- Concrete curing compounds and sealers
- Paints and Coatings
- Polymers
- Portland cement and products:
- Concrete
- Mortar (modern and historic)
- Stucco/Plaster
- Sheet and vinyl composition flooring
AASHTO and ASTM Test Capabilities
- AASHTO M 85 Chemical (Oxide) Analysis by X-ray Fluorescence (XRF)
- AASHTO M 85 Standard Specification for Portland Cement (Chemical and Physical)
- AASHTO M 157 Standard Specification for Ready-Mixed Concrete (Chemical Limitations for Mixing Water)
- AASHTO T 26 Chloride Ion in Water
- AASHTO T 26 Quality of Water to be used in Concrete
- AASHTO T 26 Quality of Water to be Used in Concrete (Solids)
- AASHTO T 105 Water Soluble Alkali Content
- AASHTO T 260 – Acid Soluble Chloride
- AASHTO T 260 Water-Soluble Chloride
- AASHTO T 290 Water Soluble Sulfate Content in Soil
- AASHTO T 291 Water Soluble Chloride Content in Soil (Method A extraction, analysis by ion specific electrode)
- AASHTO T 291 Water Soluble Chloride Content in Soil (Method B extraction, analysis by ion specific electrode)
- AASHTO T 330 Standard Method of Test for the Qualitative Detection of Harmful Clays of the Smectite Group in Aggregates Using Methylene Blue
- APHA 2540 B Total Solids Dried at 103-105 oC
- APHA 2540 C Total Dissolved Solids Dried at 180oC.
- APHA 4500Cl- (D) Chloride in Water
- ASTM C25 Chemical Analysis of Limestone, Quick lime, and Hydrated Lime (SO3)
- ASTM C25 Chemical Analysis of Limestone, Quicklime, and Hydrated Lime
- ASTM C25 Chemical Analysis of Limestone, Quicklime, and Hydrated Lime – (Available Lime)
- ASTM C114 Acid Soluble Chloride of Hydraulic Cement
- ASTM C114 Acid Soluble Sulfate
- ASTM C114 Chemical (Oxide) Analysis X-ray Fluorescence (XRF)
- ASTM C114 Chemical Analysis of Hydraulic Cement – Acid Soluble Chloroform Organic
- ASTM C114 Chemical Analysis of Hydraulic Cement (Free Calcium Oxide)
- ASTM C114 Chemical Analysis of Hydraulic Cement Section 5: Insoluble Residue
- ASTM C114 Determination of Sulfide Sulfur
- ASTM C114 Loss on Ignition
- ASTM C114 Loss on Ignition (Portland Blast Furnace Slag Cement and Slag Cement)
- ASTM C114 Sulfate (ASTM C 114 Water Soluble Alkali Extraction)
- ASTM C114 Total Alkali
- ASTM C114 Water Soluble Alkali Content
- ASTM C114 XRF Cement Content
- ASTM C115 Standard Test Method for Fineness of Portland Cement by the Turbidimeter
- ASTM C117 Materials Finer Than 75-um (no. 200) Sieve in Mineral Aggregates by Washing
- ASTM C123 Lightweight Particles in Aggregate
- ASTM C150 Standard Specification for Portland Cement
- ASTM C156 Standard Test Method for Water Loss [from a Mortar Specimen] Through Liquid Membrane-Forming Curing Compounds for Concrete
- ASTM C186 Test Method for Determination of Heat of Hydration
- ASTM C233 Standard Specification for Air-Entraining Admixtures for Concrete (ASTM C 233 Standard Test Methods for Air Entraining Admixtures for Concrete)
- ASTM C265 Water-Extractable Sulfate in Hydrated Hydraulic Cement Mortar
- ASTM C289 Standard Test Method for Potential Alkali-Silica Reactivity of Aggregates (Chemical Method – Sample Preparation)
- ASTM C309 Standard Specification for Liquid Membrane-Forming Compounds for Curing Concrete
- ASTM C311 Sampling and Testing Fly Ash or Natural Pozzolans for Use in Portland-Cement Concrete (Available Alkali)
- ASTM C311(98b) Sampling and Testing Fly Ash or Natural Pozzolans for Use as a Mineral Admixture in Portland-Cement Concrete
- ASTM C452 Sulfate Resistance
- ASTM C471 Chemical Analysis of Gypsum and Gypsum Products (Section 14 Acid Soluble SO3)
- ASTM C471 Chemical Analysis of Gypsum and Gypsum Products (Section 15 Chlorides)
- ASTM C471M Standard Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Gypsum and Gypsum Products – Section 10 (Silicon Dioxide and Other Acid Insoluble Matter)
- ASTM C494 Standard Specification for Chemical Admixtures for Concrete (Uniformity – Section 18)
- ASTM C595 Standard Specification for Blended Hydraulic Cements
- ASTM C618 Coal Fly Ash & Raw or Calcined Natural Pozzolan for Use as Mineral Admixture in Concrete
- ASTM C979 Standard Specification for Pigments for Integrally Colored Concrete
- ASTM C1017 Admixture Uniformity (Section 16, 17 and 18)
- ASTM C1084 Portland-Cement Content of Hardened Hydraulic – Cement Concrete
- ASTM C1152 Standard Test Method for Acid-Soluble Chloride in Mortar and Concrete
- ASTM C1157 Performance Specification for Hydraulic Cement
- ASTM C1218 Water-Soluble Chloride in Mortar and Concrete
- ASTM C1315 Standard Specification for Liquid Membrane-Forming Compounds Having Special Properties for Curing and Sealing Concrete
- ASTM C1324 Standard Test Method for Examination and Analysis of Hardened Masonry Mortar
- ASTM C1524 Standard Test method for Water-Extractable Chloride in Aggregate (Soxhlet Method)
- ASTM C1556 Apparent Chloride Diffusion Coefficient
- ASTM C1580 Water Soluble Sulfate in Soil
- ASTM C1602 (Table 2) Chemical Limits for Combined Mixing Water
- ASTM C1603 Standard Test Method for Measurement of Solids in Water
- ASTM C1679 Standard Practice for Measuring Hydration Kinetics of Hydraulic Cementitious Mixtures Using Isothermal Calorimetry
- ASTM C1702 Standard Test Method for Measurement of Heat of Hydration of Hydraulic Cementitious Materials Using Isothermal Conduction Calorimetry
- ASTM C1777 Standard Test Method for Rapid Determination of the Methylene Blue Value for Fine Aggregate or Mineral Filler Using a Colorimeter
- ASTM D50 Standard Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Yellow, Orange, Red, and Brown Pigments Containing Iron and ManganeseASTM D512 Chloride Ion in Water
- ASTM D806 Standard Test Method for Cement Content of Hardened Soil-Cement Mixtures
- ASTM D1208 Loss on Ignition
- ASTM D3042 Insoluble Residue in Carbonate Aggregate
- ASTM D4458 Chloride Ion in Water
- ASTM D5095 Determination of the Nonvolatile Content in Silanes, Siloxanes and Silane-Siloxane Blends used in Masonry Water Repellent Treatments
- ASTM E70 Standard Test Method for pH of Aqueous Solutions with the Glass Electrode
Other Testing Capabilities
- Color Analysis
- Free Lime
- KM 64-265-08 Kentucky Test Method for Insoluble Residue in Carbonate Aggregates
- MnDOT 1221 Determination of Acid Insoluble Residue in Limestone and Dolostone
- North Carolina DOT #C-20.0 Determination of Nitrite in Hardened Concrete
- Delayed set or strength development in concrete
Contact a Laboratory Professional
Related Services
Laboratory Projects